Understanding Interest Rates, Inflation, and Economic Indicators That Impact Markets
Introduction
Macroeconomic factors play a crucial role in shaping financial markets and investment decisions. From interest rates to inflation and key economic indicators, these elements influence stock prices, bond yields, and overall market sentiment. Understanding these factors allows investors to make informed choices and anticipate potential market trends. This blog will explore the major macroeconomic drivers and their impact on financial markets.
Macroeconomic Factors
The Role of Interest Rates
Interest rates, set by central banks like the Federal Reserve, are one of the most influential macroeconomic factors affecting financial markets.
How Interest Rates Affect Markets
- Stock Market: Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs, potentially slowing corporate growth and reducing stock prices. Lower rates can stimulate investment and boost equities.
- Bond Market: Bond prices move inversely to interest rates. When rates rise, bond yields increase, but bond prices decline.
- Consumer and Business Loans: Higher rates make loans and mortgages more expensive, reducing consumer spending and business expansion.
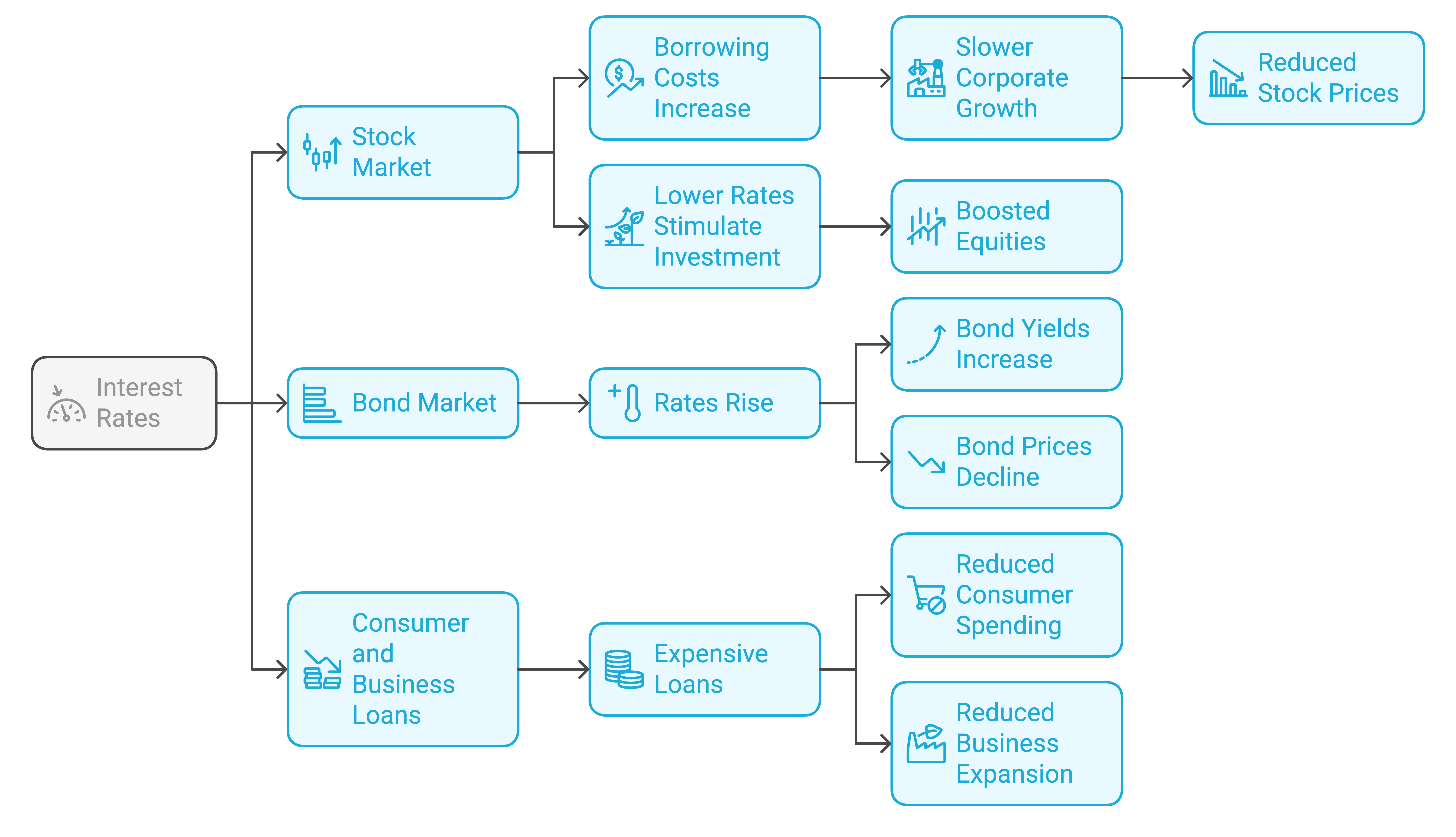
How Interest Rates Affect Markets
Central Bank Policies
Central banks adjust interest rates to maintain economic stability. For example:
- Rate hikes help control inflation but may slow economic growth.
- Rate cuts stimulate spending and investment but can lead to excessive borrowing.
Inflation and Its Market Impact
Inflation refers to the rise in prices of goods and services over time, reducing purchasing power. Moderate inflation is a sign of a healthy economy, but excessive inflation can be problematic.
Effects of Inflation on Markets
- Stock Market: High inflation can lead to increased costs for businesses, potentially reducing profit margins and affecting stock valuations.
- Bond Market: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of fixed-income returns, leading to higher yields and lower bond prices.
- Real Estate: Inflation often drives up property values, benefiting real estate investors but making housing less affordable for consumers.
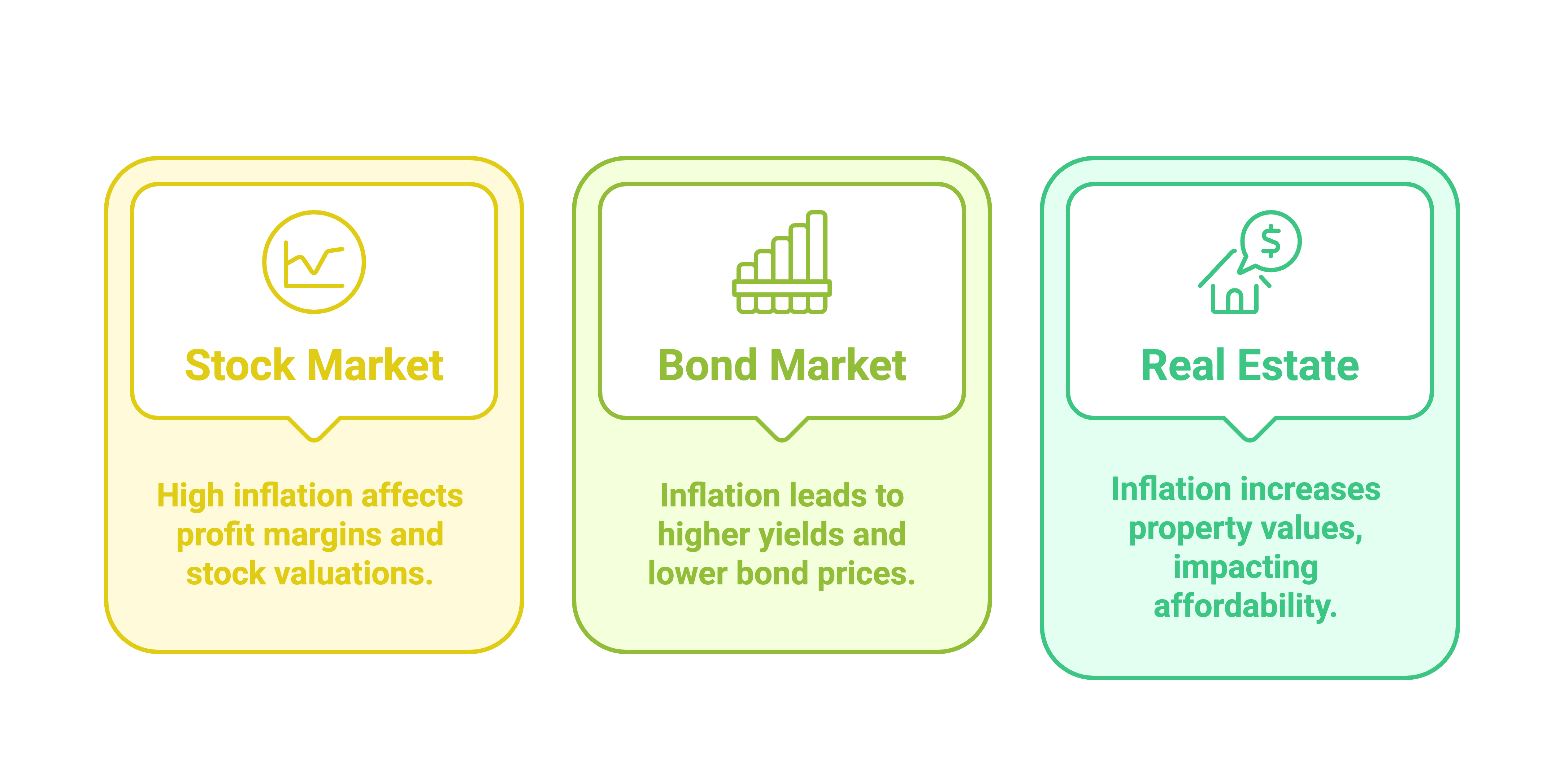
Effects of Inflation on Markets
Measuring Inflation
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): Tracks the price changes of a basket of consumer goods.
- Producer Price Index (PPI): Measures inflation at the wholesale level.
- Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE): A broader measure often preferred by the Federal Reserve.
Key Economic Indicators and Their Influence
Several macroeconomic indicators provide insights into the health of an economy and help investors gauge market direction.
1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Definition: Measures the total economic output of a country.
- Impact: A growing GDP signals a strong economy, boosting investor confidence, while a contracting GDP can indicate a recession.
2. Employment Data
- Key Reports:
- Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP)
- Unemployment Rate
- Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS)
- Impact: Low unemployment boosts consumer spending and economic growth, while high unemployment signals economic distress.
3. Consumer Confidence Index (CCI)
- Definition: Measures consumer sentiment about economic conditions.
- Impact: High consumer confidence supports spending and growth, while low confidence leads to reduced economic activity.
4. Manufacturing and Service Sector Data
- Key Reports:
- Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI)
- Industrial Production Index
- Impact: Strong manufacturing and service sector growth indicate economic expansion, while declines may signal a slowdown.
5. Trade Balance and Currency Movements
- Trade Deficit vs. Surplus: A trade surplus strengthens the domestic currency, while a deficit can weaken it.
- Exchange Rates: A strong currency benefits importers but can hurt exporters by making their goods more expensive overseas.
How Investors Can Use Macroeconomic Data
1. Asset Allocation Strategies
- During periods of low interest rates and strong GDP growth, investors may favor stocks and real estate.
- In high-inflation environments, commodities like gold and inflation-protected securities become attractive.
2. Understanding Market Cycles
- Expansion Phase: Stock prices rise, employment grows, and consumer spending increases.
- Recession Phase: Stock markets decline, unemployment rises, and central banks may cut rates to stimulate growth.
3. Monitoring Central Bank Actions
- Investors closely watch Federal Reserve meetings and policy changes to anticipate interest rate moves.
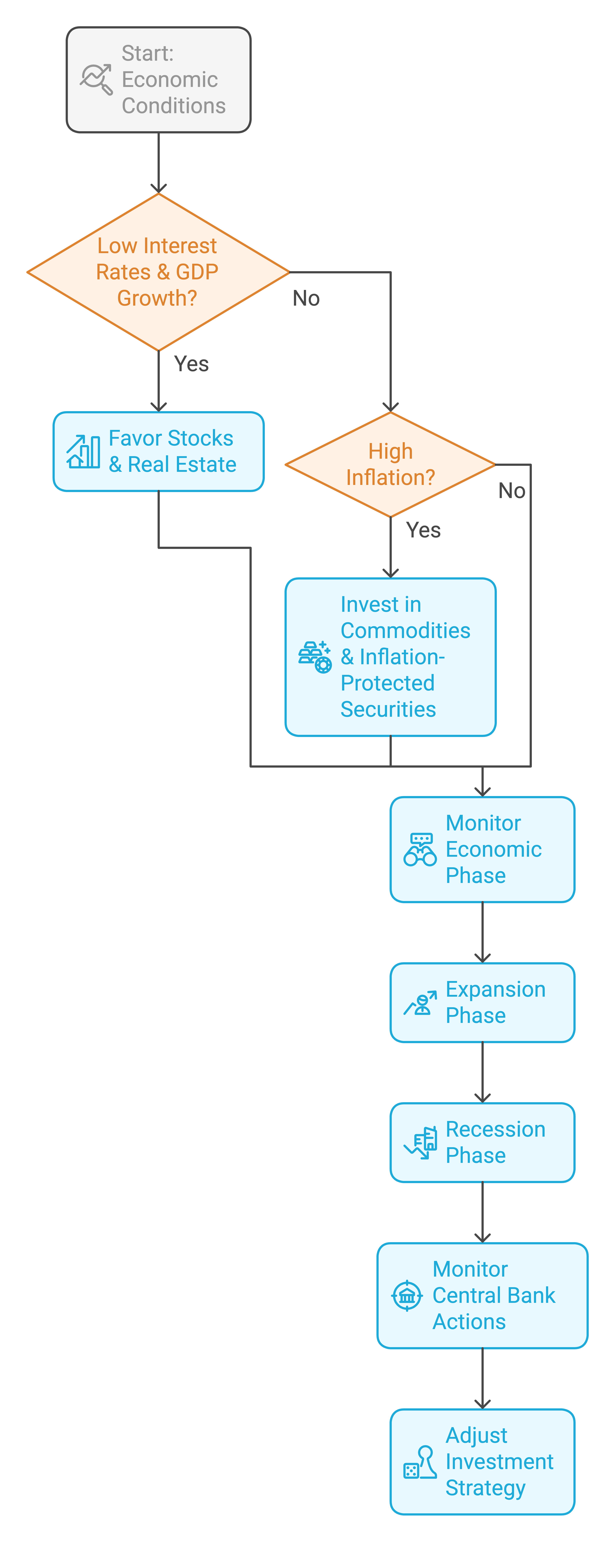
How Investors Can Use Macroeconomic Data
Conclusion
Macroeconomic factors like interest rates, inflation, and economic indicators significantly impact financial markets. By understanding these dynamics, investors can make better-informed decisions and navigate market fluctuations with confidence. Keeping an eye on key economic reports and central bank policies will provide valuable insights into future market trends and investment opportunities. If you want to track all these factors use forexfactory.com.
Key Takeaway: Staying informed about macroeconomic trends is essential for successful investing. Whether managing personal finances or trading in the stock market, understanding these factors can lead to smarter, more strategic decisions.
