What Is Forex Trading?
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange or FX trading, is the process of buying and selling currencies to make a profit. Unlike the stock market, which operates through centralized exchanges, forex trading takes place in a decentralized global marketplace where traders exchange one currency for another.
The forex market is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $7.5 trillion as of 2024. It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, across different time zones in major financial centers, including London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney.
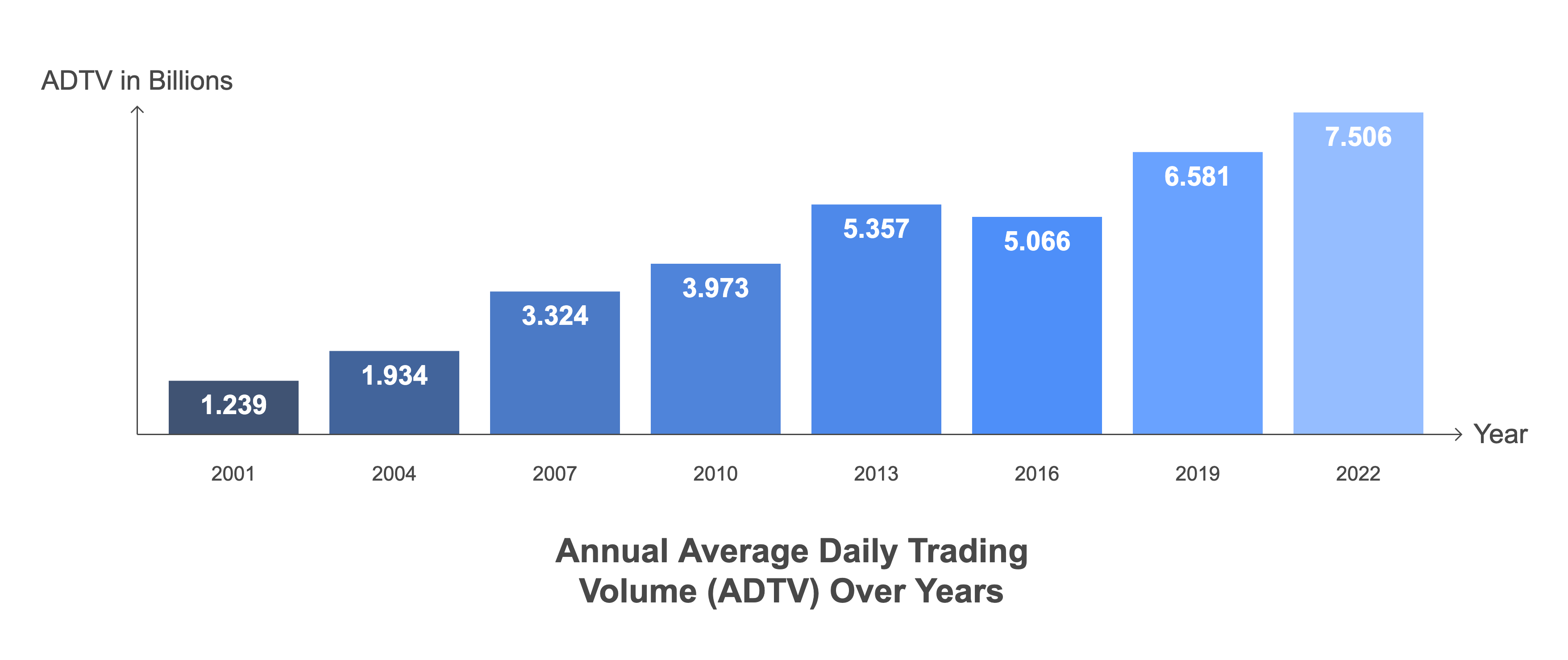
Annual Average Daily Trading Volume ADTV Over Years
Key Forex Market Statistics:
- Daily trading volume: Over $7.5 trillion
- Most traded currency pairs:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) – 28% of daily trading volume
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen) – 13%
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar) – 9%
- AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar) – 6%
- USD/CAD (US Dollar/Canadian Dollar) – 5%
- Forex market working hours:
- Sydney session: 10 PM – 7 AM GMT
- Tokyo session: 12 AM – 9 AM GMT
- London session: 8 AM – 5 PM GMT
- New York session: 1 PM – 10 PM GMT
How Forex Trading Works
Forex trading for beginners can seem overwhelming, but the basic concept is simple. Traders speculate on currency pairs, such as EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar), predicting whether one currency will strengthen or weaken against the other.
Each currency pair has a base currency and a quote currency. For example, in the EUR/USD pair:
- EUR (Euro) is the base currency.
- USD (US Dollar) is the quote currency.
If you believe the EUR will strengthen against the USD, you would buy the pair (going long). If you think the EUR will weaken against the USD, you would sell the pair (going short).
Should you buy or sell the EUR/USD pair based on currency strength?
Understanding Spreads in Forex Trading
A spread in forex trading is the difference between the bid price (the price at which you can sell a currency pair) and the ask price (the price at which you can buy a currency pair). It represents the cost of trading and is measured in pips.
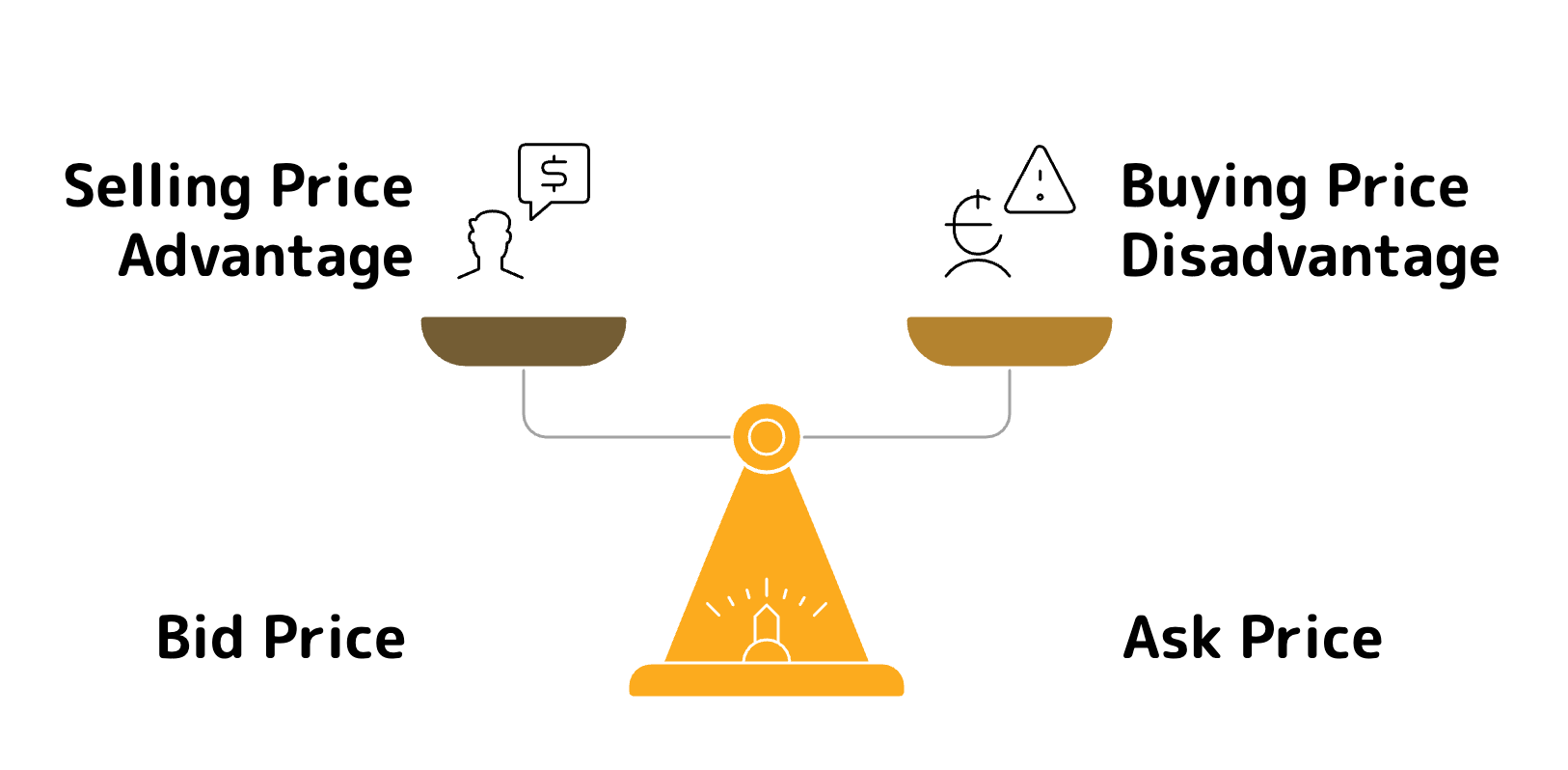
Understanding the Cost of Forex Trading
For example, if the EUR/USD currency pair has a bid price of 1.1050 and an ask price of 1.1052, the spread is 2 pips(1.1052 - 1.1050 = 0.0002 or 2 pips).
Types of Spreads:
Fixed Spread: The difference between the bid and ask price remains constant regardless of market conditions. Fixed spreads are common with brokers that act as market makers.
Variable (Floating) Spread: The spread fluctuates based on market volatility and liquidity. It is typically lower during major trading sessions and can widen during periods of high volatility.
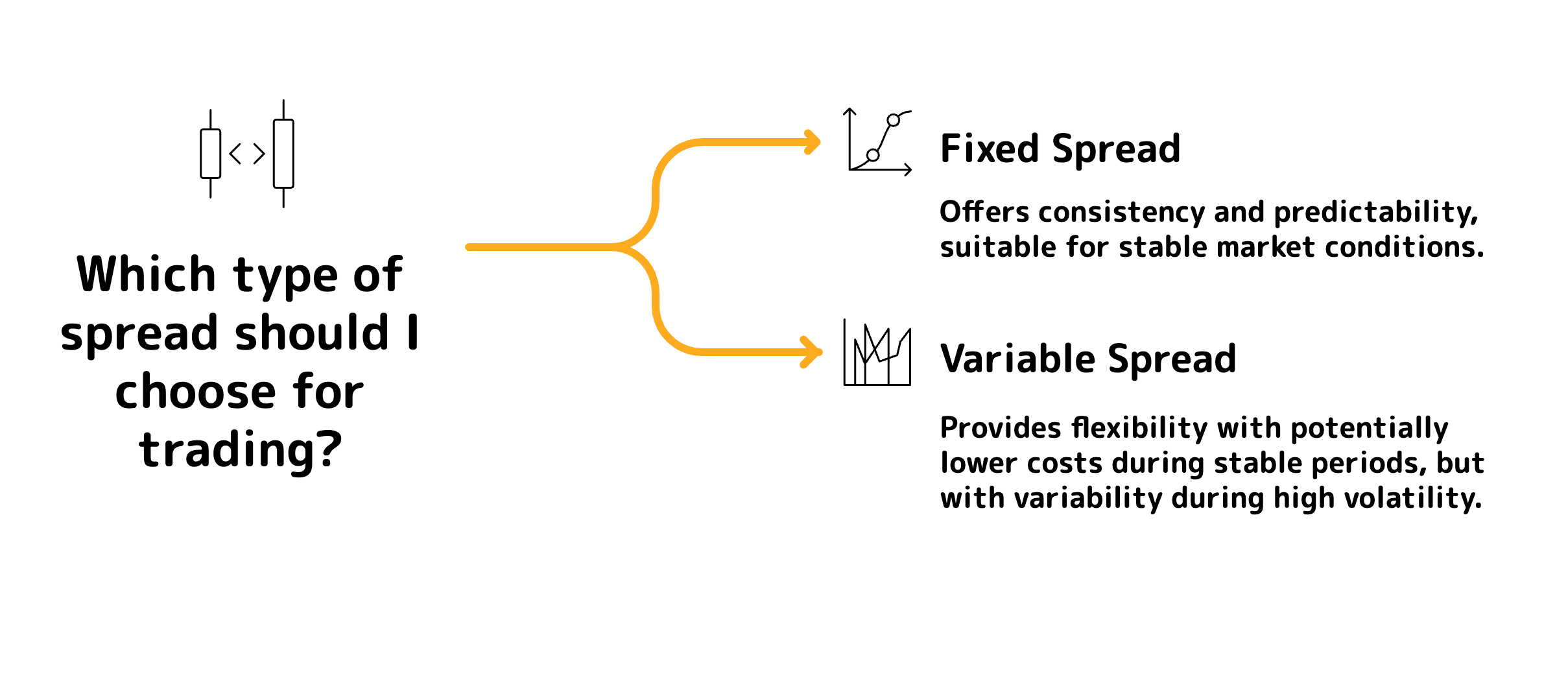
Which type of spread should I choose for trading
Why Spreads Matter:
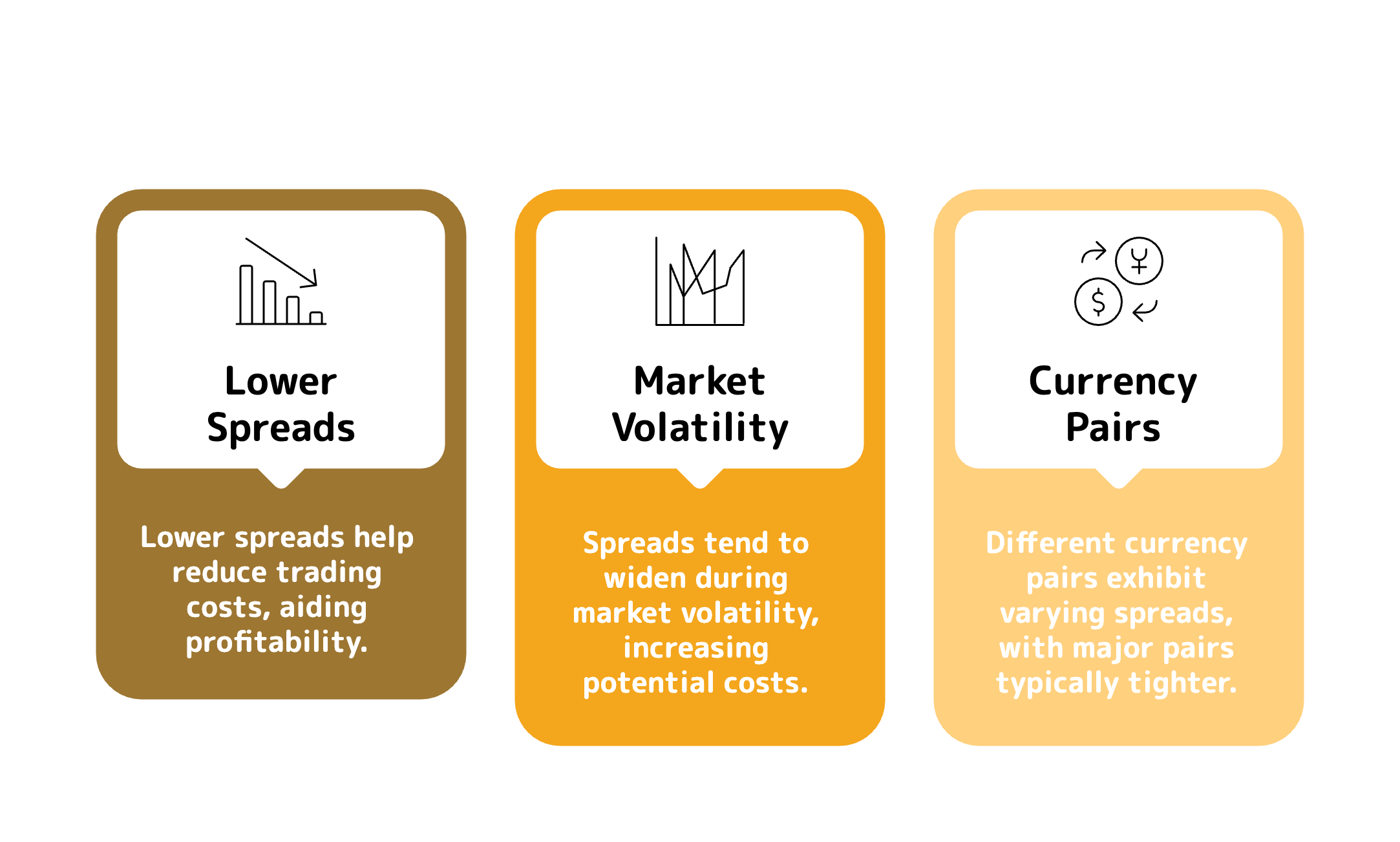
Lower spreads reduce trading costs, making it easier to achieve profitability.
Spreads widen during market volatility, so traders must be aware of potential cost increases.
Different currency pairs have different spreads, with major pairs (e.g., EUR/USD) usually having tighter spreads compared to exotic pairs (e.g., USD/TRY).
Trading Costs and Spreads
Step-by-Step Guide to Forex Trading for Beginners
Step 1: Learn Forex Trading Basics
Before jumping into live trading, it’s essential to understand fundamental concepts such as:
- Pips: The smallest price movement in forex trading.
- Lots: The size of a trade (micro, mini, or standard lot).
- Leverage: Borrowed funds that allow traders to control larger positions with a smaller capital investment.
- Margin: The amount of money required to open a leveraged position.
- Bid and Ask Price: The price at which you can sell (bid) or buy (ask) a currency pair.
Step 2: Choose a Reliable Forex Broker
A forex broker is an intermediary that provides a platform for traders to buy and sell currency pairs. Consider these factors when choosing a broker:
- Regulation: Ensure the broker is regulated by authorities like the FCA, ASIC, or CFTC.
- Trading Platform: Look for user-friendly platforms such as MetaTrader 4 (MT4) or MetaTrader 5 (MT5).
- Spreads and Fees: Lower spreads and commission fees can improve profitability.
- Customer Support: Reliable 24/5 customer service is crucial for troubleshooting issues.
Step 3: Open a Demo Account
Most brokers offer demo accounts that allow traders to practice forex trading for beginners without risking real money. Use this to:
- Familiarize yourself with the trading platform.
- Test different strategies.
- Understand risk management techniques.
Step 4: Develop a Trading Strategy
Successful forex trading requires a well-defined strategy. Some popular strategies include:
- Scalping: Making multiple small trades throughout the day.
- Day Trading: Opening and closing positions within a single trading day.
- Swing Trading: Holding positions for several days to capitalize on market swings.
- Position Trading: Long-term trading based on fundamental analysis.
Step 5: Understand Technical and Fundamental Analysis
- Technical Analysis: Involves studying price charts, indicators (such as moving averages, RSI, and MACD), and patterns to predict future movements.
- Fundamental Analysis: Focuses on economic indicators, news events, interest rates, and geopolitical developments that impact currency values.
Step 6: Manage Risk Effectively
Risk management is critical in forex trading for beginners. Some essential risk management practices include:
- Using Stop-Loss Orders: Automatically closes a trade at a predefined price to limit losses.
- Position Sizing: Never risk more than 1-2% of your trading capital on a single trade.
- Avoiding Over-Leverage: While leverage increases profit potential, it also magnifies losses.
Step 7: Start Trading with a Live Account
Once comfortable with demo trading, transition to a live trading account with a small capital investment. Begin with minimal risk and gradually increase your position size as you gain confidence.
Step 8: Continuously Learn and Improve
Forex trading is an ongoing learning process. Stay updated with market trends, economic news, and new trading strategies by:
- Reading forex trading books and blogs.
- Watching educational videos and webinars.
- Joining online trading communities and forums.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Forex Trading
- Lack of a Trading Plan: Trading without a clear plan leads to impulsive decisions and losses.
- Ignoring Risk Management: Failing to use stop-loss orders or over-leveraging can wipe out your capital.
- Emotional Trading: Letting emotions drive decisions often results in poor judgment.
- Overtrading: Excessive trading increases transaction costs and risks.
- Neglecting Market Analysis: Skipping technical and fundamental analysis reduces the chances of making informed trades.
Final Thoughts
Forex trading for beginners can be both exciting and challenging. By understanding the basics, choosing a reliable broker, developing a trading strategy, and practicing risk management, you can build a strong foundation for success in the forex market.
Remember, patience and continuous learning are key to becoming a successful forex trader. Start small, stay disciplined, and refine your strategy over time. Happy trading!
